
In our daily lives, we encounter countless microorganisms, some of which can be harmful to our health. The body has a remarkable defense system known as immunity, which safeguards us from infections and diseases. This immunity comes in various forms, each playing a crucial role in protecting our well-being.
What Is Immunity
Immunity refers to the body's ability to resist or defend against infections, diseases, or harmful substances. It is a complex system of biological processes and structures that work together to identify and neutralize foreign invaders, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other pathogens.
The immune system is composed of various components, including specialized cells, tissues, and organs, that work in coordination to protect the body. These components recognize and respond to specific substances, known as antigens, that are present on the surface of pathogens.
4 Different Types of Immunity In Human Body
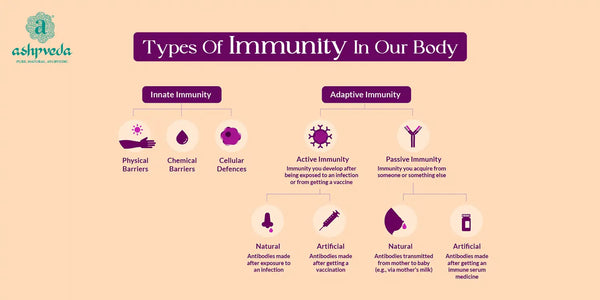
1. Innate Immunity: Nature's First Line of Defense
Innate Immunity Overview
At the forefront of our body's defense arsenal lies innate immunity. This is the first line of defense we possess, offering immediate protection against a wide range of pathogens. Unlike adaptive immunity, which develops over time, innate immunity is pre-existing and does not require prior exposure to a specific threat.
Types Of Innate Immunity
- Physical Barriers
-
- Skin: Our body's largest organ, serving as a formidable barrier against pathogens.
- Mucous Membranes: Found in the respiratory, digestive, and reproductive tracts, they secrete mucus to trap and eliminate invaders.
- Cellular Defenses
-
- Phagocytes: Specialized white blood cells that engulf and destroy pathogens.
- Natural Killer Cells: These cells target and eliminate infected or abnormal cells.
- Inflammatory Response
- A rapid and localized reaction to tissue injury or infection, characterized by redness, swelling, heat, and pain.
Read Also: Health Benefits Of Chyawanprash
2. Adaptive Immunity: Tailored Protection for Targeted Threats
Adaptive Immunity Overview
While innate immunity provides immediate protection, adaptive immunity takes a more precise approach. This type of immunity develops over time, as the body encounters and learns to recognize specific pathogens. Once primed, the adaptive immune system mounts a targeted and highly effective defense against these familiar foes.
Components of Adaptive Immunity
- Lymphocytes
-
- B Cells: Produce antibodies that neutralize pathogens.
- T Cells: Coordinate immune responses and directly destroy infected cells.
- Immunological Memory
- After an initial exposure to a pathogen, the immune system "remembers" it, enabling a quicker and more robust response upon future encounters.
Read Also: Benefits Of Satavari
3. Passive Immunity: Borrowed Shields for Immediate Protection
Passive Immunity Overview
In certain situations, our bodies can acquire temporary immunity from external sources. This is known as passive immunity. Unlike innate and adaptive immunity, which are acquired through natural processes, passive immunity is conferred through external means.
Forms of Passive Immunity
- Maternal Antibodies
-
- Newborns receive antibodies from their mothers via the placenta or breast milk, providing crucial protection in the early stages of life.
- Immunotherapy
- Administration of pre-formed antibodies or immune components to confer immediate protection against specific pathogens.
Read Also: Health Benefits Of Amla
4. Mucosal Immunity: Guardian of Mucous Membranes
Mucosal Immunity Overview
Mucosal surfaces, such as those lining the respiratory and digestive tracts, represent primary points of contact with the external environment. Mucosal immunity specializes in safeguarding these vulnerable entry points from potential threats.
Key Players in Mucosal Immunity
- Secretory IgA Antibodies
-
- These antibodies are secreted onto mucosal surfaces, forming a protective barrier against pathogens.
- Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT)
- Specialized immune tissues strategically located near mucosal surfaces, facilitate rapid immune responses.
Read Also: Health Benefits Of Matcha Tea Powder
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of immunity in our body sheds light on the intricate defense mechanisms that keep us healthy. From our innate defenses to the tailored protection of adaptive immunity, each type plays a vital role in safeguarding our well-being.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. Can I have both innate and adaptive immunity at the same time?
Yes, our body employs both innate and adaptive immunity simultaneously to provide comprehensive protection.
2. How long does passive immunity last?
Passive immunity is temporary and typically lasts for a few weeks to a few months.
3. Can vaccination lead to active immunity against a disease?
Yes, vaccines stimulate the body to develop active immunity without causing the disease itself.
4. What are some common immune disorders?
Common immune disorders include autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and allergies.
5. How can I support my immune system through nutrition?
Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can bolster your immune health.
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.

